Dexamethasone Implants Could Preserve Vision Longer for Diabetic Macular Edema Patients Post & News admin November 3, 2023 Newswise — Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a significant complication of diabetes, often leading to vision loss. A recent review paper published in the journal Pharmaceutics provides evidence-based recommendations on using intravitreal dexamethasone implants (DEX) for treating DME. DEX is a corticosteroid implant that reduces inflammation and fluid accumulation in the retina.The paper was authored by an international team of researchers working with the Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO) under the leadership of Antonio Giordano, M.D., Ph.D., Founder and Director of SHRO. The authors suggest considering DEX as a first-line strategy in certain situations. For instance, patients with signs of inflammation or have had eye surgery.DME occurs when fluid accumulates in the macula – the central part of the retina responsible for sharp and detailed vision. Despite significant advancements in therapeutic management, DME remains a clinical challenge due to the increasing global prevalence of diabetes.The authors also recommend DEX for patients with recent cardiovascular events like heart attacks or strokes. These patients may have an increased risk of bleeding or thrombosis from anti-VEGF injections. Pregnant women needing urgent treatment to prevent vision loss and patients scheduled for cataract surgery or with poor compliance with frequent injections might also benefit from DEX.Other aspects analyzed for DME treatment with DEX include when to start, switch, or stop DEX therapy based on factors like visual acuity, retinal thickness, intraocular pressure, and more. The review explores whether combining DEX with laser photocoagulation could enhance the effect or reduce side effects of either therapy. It also addresses how to manage the association between glaucoma and DEX therapy since corticosteroids can increase eye pressure and damage the optic nerve. Additionally, it discusses the use of DEX implants in patients with DME undergoing cataract surgery. Because DME likely increases after surgery, the injection of a DEX implant preop or at the same time is highly recommended as it was shown to prevent DME or keep it from worsening.“The use of dexamethasone implants in treating diabetic macular edema presents an opportunity for personalized treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics and responses to therapy,” says Giordano. “As our understanding of DME continues to evolve, so too will our therapeutic approaches, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.”About the Sbarro Health Research Organization The Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO) is non-profit charity committed to funding excellence in basic genetic research to cure and diagnose cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and other chronic illnesses and to foster the training of young doctors in a spirit of professionalism and humanism. To learn more about the SHRO please visit www.shro.org. Previous Post
Category: Post & News
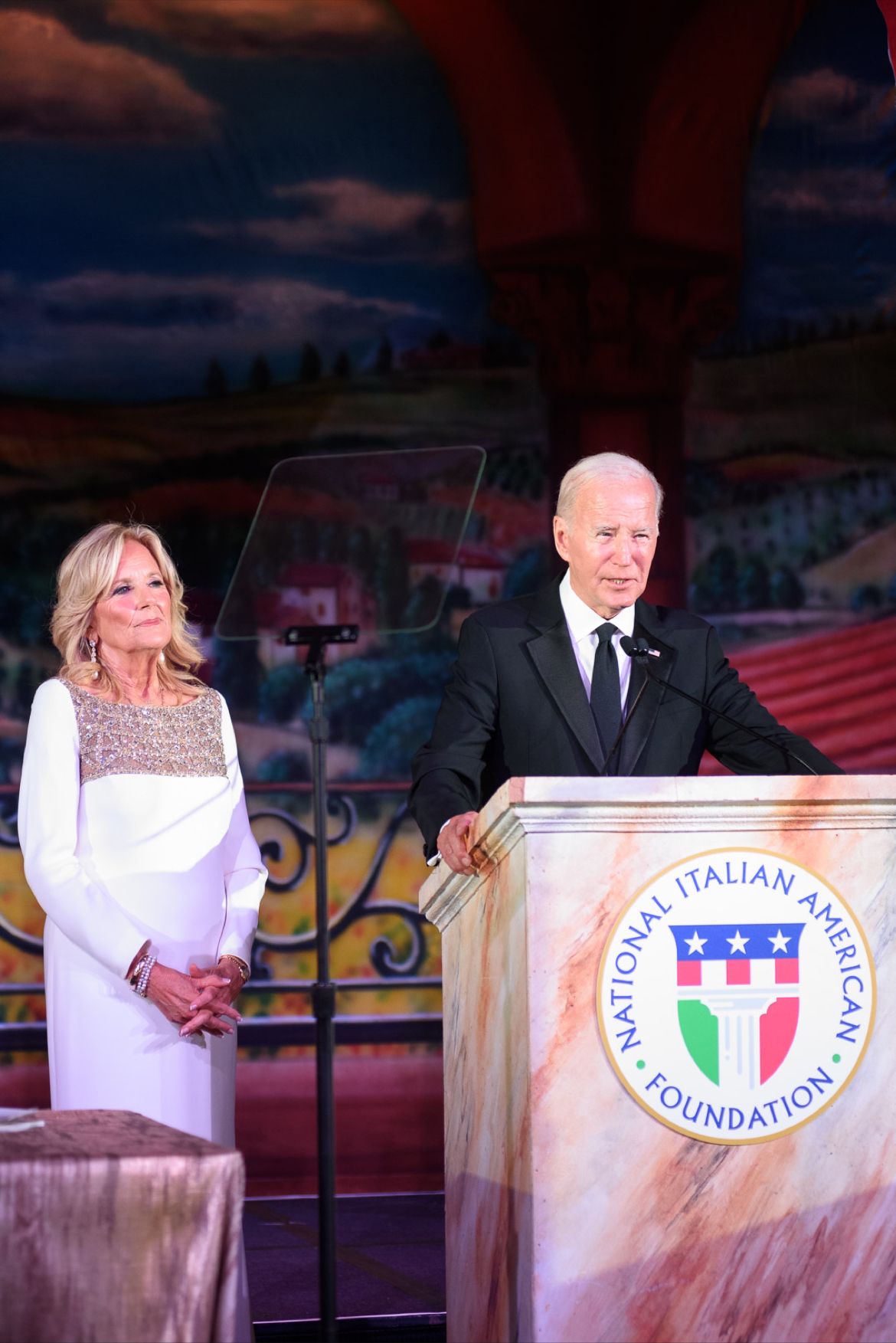
First Lady Surprises At The NIAF 48th Anniversary Gala by inviting President Joe Biden
First Lady Surprises At The NIAF 48th Anniversary Gala At the gala event NIAF celebrates and honors the Italian American heritage Post & News admin October 18, 2023 The National Italian American Foundation (NIAF) celebrated it’s 48th Anniversary amidst the attendance of 900 Italian and American guests marking its huge success on Sunday, 14th October 2023. The night was full of fun, delicious cuisine, and a genuine love for Italian heritage and culture.One of the great highlights of the event was attendance of the First Lady. The First Lady gave a moving speech in which she conveyed her gratitude to the group and lauded the extraordinary accomplishments of Italian Americans, especially the awardees for the evening.In a heartwarming twist, the First Lady unexpectedly extended an invitation to the President Joe Biden, who politely accepted, and spoke to the already mesmerized audience. His speech touched on the important contribution and unyielding spirit of the Italian American community, guaranteeing that people would remember this occasion for years to come. Among those honored at the event were Veronica Berti Bocelli, CEO of Almud Music Editions and Vice-Chair of the Andrea Bocelli Foundation; Dr. Stefano Domenicali, President & CEO of Formula 1®; Gerry Cardinale, Founder & Managing Partner of RedBird Capital Partners; Neil Giraldo; and Sara Farnetti, PhD. As board member Professor Antonio Giordano, MD, PhD, Founder & Director of the Sbarro Health Research Organization, was among the panel who presented the awards to the honorees. The 48th Anniversary of the National Italian American Foundation also saw the successful hosting of the medical conference “The Future is Here! Brought to you by Italian Scientists: Improving Cancer Care and Health with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning”, by Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO), in collaboration with Giovan Giacomo Giordano Foundation, Temple University, and NIAF. Michele Ceccarelli, Ph.D., and Giorgio Ventre, Ph.D., received the ‘Giovan Giacomo Giordano NIAF Lifetime Achievement Award for Ethics and Creativity in Medical Research’ during the conference in recognition of their years of commitment and service. Events like this are crucial in a world when it’s simple to forget one’s history and roots. They serve as a reminder of our origins, the challenges that our ancestors overcame, the achievements that they celebrated, and the exciting future that lies ahead. Previous Post
AI Discussion at International Medical Conference Presented by Sbarro Health Research Organization
AI Discussion at International Medical Conference Presented by Sbarro Health Research Organization Post & News admin October 13, 2023 Newswise— Top Italian Scientists join the discussion of AI and Machine Learning presented by the Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO) in collaboration with the National Italian American Foundation (NIA) this weekend at the annual NIAF convention and gala. The event will cover the use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms in cancer diagnosis, therapy, and medicine is rapidly being adopted in the clinical setting. Currently, these technologies are making an immediate impact on our ability to correctly detect, diagnose, and treat diseases like cancer, heart disease, and even infertility, improving patient’s lives. This symposium will feature how expert Italian and Italian/American clinicians are using AI and machine learning in their medical practices, and what future advances in this technology will mean for your healthcareThe Future is Here! brought to you by Italian Scientists: Improving Cancer Care and Health with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Saturday, October 14 09.00am | 10.15 am Executive Room Omni Shoreham Hotel 2500 Calvert Street NW Washington, DC Organizing Committee Giancarlo Arra – Vice President SHRO Antonio Giacomini – Ceo Innovaway S.p.A Luciano Dolgetta – Board Member SHRO Andrew Douglas – Board Member SHRO Robert V. Allegrini – Board Member NIAF Joseph del Raso – Board Member NIAF Joseph Gulino – Board Member NIAF Bob Carlucci – Board Member NIAF Massimo Petrone – Board Member NIAF Program and Speakers Opening Remarks Antonio Giordano – MD, PhD President of Sbarro Health Research Organization, Philadelphia, PA Can we leave AI just to Geeks? Giorgio Ventre – PhD Scientific Director, Apple Developer Academy, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e delle Tecnologie dell’Informazione, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II, Naples, Italy Artificial intelligence and big data in cancer and precision oncology: using data to understand the molecular basis of cancer Michele Ceccarelli – PhD Professor, Program Leader of Computational Oncology at the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Miami, Miami, FL Presentation of the Giovan Giacomo Giordano NIAF award for ethics and creativity in medical research Giovan Giacomo Giordano, Jr. Strategic Finance, PepsiCo, New York, New York About the Sbarro Health Research Organization The Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO) is non-profit charity committed to funding excellence in basic genetic research to cure and diagnose cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and other chronic illnesses and to foster the training of young doctors in a spirit of professionalism and humanism. To learn more about the SHRO please visit www.shro.org. Previous Post
The Future is Here! Brought to you by Italian Scientists: Improving Cancer Care and Health with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning” Medical Conference
The Future is Here! Brought to you by Italian Scientists: Improving Cancer Care and Health with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning” Medical Conference Post & News admin October 7, 2023 The Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO), in collaboration with Temple University’s College of Science and Technology, the National Italian American Foundation (NIAF), and the Giovan Giacomo Giordano Foundation will host the medical conference “The Future is Here! Brought to you by Italian Scientists: Improving Cancer Care and Health with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning” 9 A.M on Saturday, October 14th at the Omni Shoreham Hotel in Washington, D.C.The conference will feature introductions presented by SHRO’s President Antonio Giordano who is also director of Temple’s Sbarro Institute for Cancer Research and Molecular Medicine and Center for Biotechnology Temple and CST are leaders in biotech research and development, and recently launched masters programs in both bioinnovation and biotechnology.Guest speakers include Michele Ceccarelli, Ph.D. and Giorgio Ventre, Ph.D. Dr. Ceccarelli will address “Artificial Intelligence and big data in cancer and precision oncology: using data to understand the molecular basis of cancer”. Dr. Ventre will discuss “Can we leave AI just to Geeks?”. The conference will culminate in the presentation of the 2018 Giovan Giacomo Giordano NIAF Lifetime Achievement Award for Ethics and Creativity in Medical Research by Mr. Giovan Giacomo Giordano Jr. , designed by artist Lello EspositoEsposito. This award was established seven years ago in honor of Dr. Giordano’s father, the late Professor Giovan Giacomo Giordano, renowned pathologist and former chair of the Department of Pathology, Second University of Naples, who dedicated more than sixty years of his life to the study of cancer and the role of environmental factors in the onset of this disease. Professor Giovan Giacomo Giordano was also a major advocate against corruption in the Italian medical community and driving force for the establishment of medical ethical standards among his colleagues. The award will be presented to Dr. Ceccarelli and Dr. Ventre for their years of dedication and service. Previous Post
Blood Thinners Have Role in Cancer Care to Prevent Embolism
Blood Thinners Have Role in Cancer Care to Prevent Embolism Post & News admin September 13, 2023 Newswise — Analysis of anticoagulants in patients with malignant cancer shows that further study is needed to establish an adjuvant, or combined, treatment protocol. Cancer patients are at a high risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE), and cancer-related thromboembolic events have emerged as the second-leading cause of death in patients undergoing chemotherapy.TResearchers working with Sbarro Health Research Organization (SHRO) under the leadership of Professor Antonio Giordano, M.D., Ph.D., recently analyzed the relationship between cancer, inflammation and vascular thrombotic diseases. This review examined all of the available experimental data about the antiinflammatory and anticancer effects of the most commonly used anticoagulant therapies in patients with malignancy. The authors conclude that the pleiotropic effects of anticoagulants are of significant interest and should be considered alongside drug–drug interactions and benefit/risk balance of drugs.The paper, “Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects of Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Malignancy,” was recently published in the journal Life.”Dedicated and continuous efforts should be made to coordinate medical education and training and to promote clinical research in cardio-oncology,” says Giordano, President of SHRO. “Because cardio-oncology care is a growing field, there is need for proper fellowship programs to train cardiologists in cancer-cardiovascular care””Before starting the anticoagulation therapy, a careful cardio-oncologic evaluation is required,” says co-author Professor Vincenzo Russo, M.D., Ph.D., University of Campania, “as patients with gastrointestinal and genitourinary malignancy showed an increased risk of major bleeding. A patient-centered approach based on the clinical characteristics and biomarker evaluation may help clinicians to choose the optimal anticoagulation strategy in patients with malignancy.” Previous PostNext Post